ATOMA
(greek
for indivisible)
1808 Jhon Dalton
Suggested
that all matter was made up of tiny apheres that were able to bounce around
with perfect elasticity and called them
ATOMS
1898
Joseph Jhon Thompson
Found
that atoms could eject a for smaller negative which he called on
ELECTRON
1904
Thompson
develops the idea that an atom was made up of electrons scattered unevenly with
in an elastic sphere surrounded by a soup of positive charge to balance the
electron’s charge like plums surrounded by pudding
1910
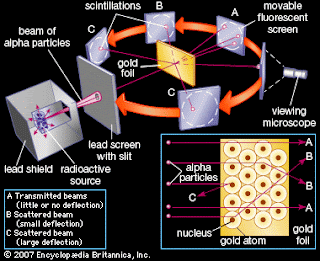
Ernest Rutherford
Oversaw
Geiger and Marsden carrying out his famous experiment They fired Helium nuclei
at a plece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick They found that
atthough most of them passed through. About 1 in 10000 hit.
They
found that while most of the helium nuclei passed through the foil, a small
number were deflected and, to their surprise, some helium nucled bounced
straight back.
Rutherford’s
new allowed him to propose a more detailed model with a central nucleus.
He
suggested thet the positive charge was all in a central nucleus. With this
holding the electrons in place by electrical attraction.
However, this was not the end of
the story.
1913
Niels Bohr
Studied
under Rutherford at the Victoria University in Manchester
Bohr
refined Rutherford’s idea by adding that the electrons were in orbits. Rather
like planets orbiting the sun. With each orbit only able to contain a set
number of electrons.
Helium Atom
What
do these particles consist of?
Buat Facebook Comment, klik







Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar